Neurotransmitters, Ion Channel and Efferents (NICE) Sub-group
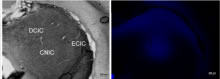
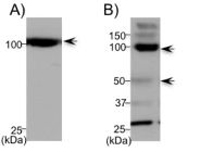
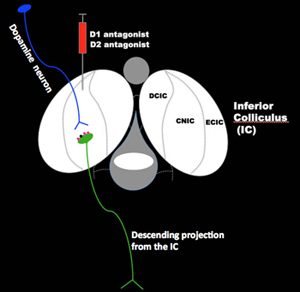
Hearing loss and tinnitus have been linked to changes in spontaneous neuronal activity in auditory brain regions. These changes in neuronal activity suggest modulation of neurotransmitter signaling, possibly through voltage gated calcium channels. One focus of our group is to examine the effect of modulation of voltage gated calcium channels on susceptibility to hearing loss and tinnitus. In this study, we are interested in whether tinnitus perception and spontaneous neuronal activity are attenuated by L- and N-type voltage gated calcium channel blockers. Thus, these blockers are examined as a possible preventative therapy for noise induced tinnitus and hearing loss. Another area of interest is the role of dopamine neurotransmission in auditory processes. Although dopamine has been extensively studied for its involvement in learning and neurological disorders, its role in auditory processes is not well understood. Utilizing gene expression, immunocytochemistry, Western immunoblotting, tract tracing, and pharmacological assays, we evaluate the role dopamine transmission plays in hearing processes in the inferior colliculus.
 |  |  |